Dec. 19 - Dec. 21
We are in the final stretch! We will review for the semester final on Monday.
Tuesday and Wednesday are half days. Testing will be going on both of those days. Exam days are as follows:
Tuesday - Periods 1 & 2
Wednesday - Periods 3 & 4
Enjoy the Holiday Break!
Friday, December 16, 2016
Sunday, December 11, 2016
Friday, December 2, 2016
DEC. 7-DEC.11
Students will need to bring a flash drive to school this week so they can save their work from this semester. An 8 gigabyte flash drive should be enough and nowadays cost about $5.00. We will be creating a reel including some of their best work from the semester and will then save all of the work created on their flash drive.
We will also watch some videos on how different special effects are created on some popular tv shows and movies.
Students will need to bring a flash drive to school this week so they can save their work from this semester. An 8 gigabyte flash drive should be enough and nowadays cost about $5.00. We will be creating a reel including some of their best work from the semester and will then save all of the work created on their flash drive.
We will also watch some videos on how different special effects are created on some popular tv shows and movies.
Friday, November 11, 2016
Friday, November 4, 2016
WEEK OF 11/7-11/11
On Monday we will watch the News Stories students created in class. We then will go over the expectations for our latest project a Music Video. You can find more information on the project on my website: https://sites.google.com/site/mrstheriaultstvproductionclass/my-forms
On Monday we will watch the News Stories students created in class. We then will go over the expectations for our latest project a Music Video. You can find more information on the project on my website: https://sites.google.com/site/mrstheriaultstvproductionclass/my-forms
Sunday, October 30, 2016
WEEK OF OCT. 31 - NOV. 4
Students should be finishing recording, writing, voicing and editing their news stories. Projects are due Thursday. We will also have a test on Friday 11/4 over various jobs in a newsroom. Here is the list of jobs you need to know for the test:
Students should be finishing recording, writing, voicing and editing their news stories. Projects are due Thursday. We will also have a test on Friday 11/4 over various jobs in a newsroom. Here is the list of jobs you need to know for the test:
CAREERS IN TELEVISION, DOCUMENTARIES & PUBLIC SERVICE
ANNOUNCEMENTS:
graphic
designer - conveys information visually through the use of color,
graphics, images, and animation that support the script.
news
director - Manages newsroom staff. Demonstrates many skills, including writing, editing,
interviewing and announcing news coverage of all types.
producer and assistant producers - decides which stories to cover
in a news program and coordinates the details of the program
camera
crew takes video footage of an event for a television broadcast
assignment editor-monitors scanners, manages news crews, makes beat
checks and generates story ideas.
script writer - works with the producer and the
reporters to develop a fluent narration of scripts that keeps the show
moving.
reporter - researches a topic, interviews key players, and
presents his or her findings on a television news program
newscaster
or news anchor - presents a news show on television, radio or the
Internet.
lighting
director
- Responsible for designing, arranging and controlling all lighting.
audio
mixer/sound mixer/sound supervisor - Responsible for sound
balance of a program. They are in
charge of determining the number of microphones and their placement required
for the production.
editor - Selects,
compiles and cuts video and audio to produce programs. They may assemble clips and segments
into programs.
set
designer
- Responsible for conceiving, designing and organizing sets for a production.
director- visualizes
the script by instructing camera operators on the type of shots wanted then
selects the best shots for the final production.
floor
manager
- Cues talent and directs the floor crew.
Responsible for organization, safety and security in the studio.
stereographer
-
The camera operator of 3D film or one who supports 3D equipment in a 3D film.
List 5
jobs that use video: Where is video used?
*News
*Advertising
industry
*Motion
picture studios
*Law
firms - taping testimony or creating video wills
*Real
Estate-video tours of homes and properties
*Education
- lessons, projects, athletic events
*Weddings
*Corporations
- presentations, training
*Music
industry
*Insurance-videotaping
contents or homes or damage after a
storm
*Law
enforcement/Armed Services - training
Friday, October 21, 2016
Friday, October 14, 2016
Week of 10/17
Due to various technical issues our Talk Show project due date will now be 10/20. All projects must be completed by the end of the class period.
We will have our test on the Adobe Premiere Shortcuts on Friday 10/21. The vocab is posted on my website and also below:
https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnxtcnN0aGVyaWF1bHRzdHZwcm9kdWN0aW9uY2xhc3N8Z3g6MTI3MGMwY2RkMWEwZDJl
ADOBE PREMIERE SHORT CUT KEYS:
Q – Trims a video at the beginning
W – Trims video at the end
L- plays forward in timeline
J - plays backwards in timeline
K + L - plays forward in slow motion
K + J - plays backward in slow motion
G - allows you to adjust the audio gain
[ Bracket decrease clip volume
] Increase clip volume
Command L – Links clips together
Command T – Title
Command Z - Undo
Command D – Apply Video Transition
Shift + Command + D – Apply Audio Transition
Command S - Save
Shift D – Places the default transition in a clip
Hold the Command key as you are moving clips over and it pushes the other clips that were in the new
position over.
Option + Delete – causes everything to slide over and clip is removed from the timeline.
Command + Arrows Allows you to nudge clip over frame by frame.
Double Click on the scroll bar to see the whole timeline sequence.
Due to various technical issues our Talk Show project due date will now be 10/20. All projects must be completed by the end of the class period.
We will have our test on the Adobe Premiere Shortcuts on Friday 10/21. The vocab is posted on my website and also below:
https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnxtcnN0aGVyaWF1bHRzdHZwcm9kdWN0aW9uY2xhc3N8Z3g6MTI3MGMwY2RkMWEwZDJl
ADOBE PREMIERE SHORT CUT KEYS:
Q – Trims a video at the beginning
W – Trims video at the end
L- plays forward in timeline
J - plays backwards in timeline
K + L - plays forward in slow motion
K + J - plays backward in slow motion
G - allows you to adjust the audio gain
[ Bracket decrease clip volume
] Increase clip volume
Command L – Links clips together
Command T – Title
Command Z - Undo
Command D – Apply Video Transition
Shift + Command + D – Apply Audio Transition
Command S - Save
Shift D – Places the default transition in a clip
Hold the Command key as you are moving clips over and it pushes the other clips that were in the new
position over.
Option + Delete – causes everything to slide over and clip is removed from the timeline.
Command + Arrows Allows you to nudge clip over frame by frame.
Double Click on the scroll bar to see the whole timeline sequence.
Monday, October 10, 2016
Week of October 10th
Can we talk????? Students are going to be learning about how the Talk Show format has been in existence since Televisions existed in the United States. They will then have to create their own short talk show segment.
Short cut keys test 10/21
Can we talk????? Students are going to be learning about how the Talk Show format has been in existence since Televisions existed in the United States. They will then have to create their own short talk show segment.
Short cut keys test 10/21
ADOBE PREMIERE SHORT CUT KEYS:
Q – Trims a video
at the beginning
W – Trims video
at the end
L- plays forward in timeline
J - plays
backwards in timeline
K + L - plays
forward in slow motion
K + J - plays backward in slow motion
G - allows you to
adjust the audio gain
[ Bracket
decrease clip volume
] Increase clip volume
Command L – Links
clips together
Command T – Title
Command Z - Undo
Command D – Apply
Video Transition
Shift + Command + D
– Apply Audio Transition
Command S - Save
Shift D – Places
the default transition in a clip
Hold the Command key
as you are moving clips over and it pushes the other clips that were in the new
position over.
Option + Delete –
causes everything to slide over and clip is removed from the timeline.
Command + Arrows
Allows you to nudge clip over frame by frame.
Double Click on the scroll bar to see the whole timeline
sequence.
Week of October 10th
Can we talk????? Students are going to be learning about how the Talk Show format has been in existence since Televisions existed in the United States. They will then have to create their own short talk show segment.
Short cut keys test 10/19
Can we talk????? Students are going to be learning about how the Talk Show format has been in existence since Televisions existed in the United States. They will then have to create their own short talk show segment.
Short cut keys test 10/19
ADOBE PREMIERE SHORT CUT KEYS:
Q – Trims a video
at the beginning
W – Trims video
at the end
L- plays forward in timeline
J - plays
backwards in timeline
K + L - plays
forward in slow motion
K + J - plays backward in slow motion
G - allows you to
adjust the audio gain
[ Bracket
decrease clip volume
] Increase clip volume
down
Command L – Links
clips together
Command T – Title
Command Z - Undo
Command D – Apply
Video Transition
Shift + Command + D
– Apply Audio Transition
Command S - Save
Shift D – Places
the default transition in a clip
Hold the Command key
as you are moving clips over and it pushes the other clips that were in the new
position over.
Option + Delete –
causes everything to slide over and clip is removed from the timeline.
Command + Arrows
Allows you to nudge clip over frame by frame.
Double Click on the scroll bar to see the whole timeline
sequence.
Sunday, October 2, 2016
Friday, September 16, 2016
This week: 9/19-9/23
We will take a test on Tuesday on the Advertising Literacy Vocab that was handed out to students last week. If you've lost your paper, here are the terms you need to know: (They can also be found on my website https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnxtcnN0aGVyaWF1bHRzdHZwcm9kdWN0aW9uY2xhc3N8Z3g6MzFhNjA2YTYxZDVjODUwMQ
We will take a test on Tuesday on the Advertising Literacy Vocab that was handed out to students last week. If you've lost your paper, here are the terms you need to know: (They can also be found on my website https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnxtcnN0aGVyaWF1bHRzdHZwcm9kdWN0aW9uY2xhc3N8Z3g6MzFhNjA2YTYxZDVjODUwMQ
ADVERTISING LITERACY VOCAB:
I. Advertising:
Tool used to get people to want to buy something. Created mainly to sell
something.
A. Found On: Television, Radio, Newspapers, Magazines,
Mailers, Billboards, Internet, Movie Theater, Buses, Bus stop benches, etc…
B. Advertisers pay money to television networks or radio and
internet to run their ads. The money paid, helps pay for the cost of programs
on television, radio and online.
C. Advertisements give people information about a product to
help them decide what to buy.
D. Consumer: Someone who buys and uses products and services
E. Federal Trade Commission (FTC): Government agency works
to protect consumers from being hurt by advertising. Requires claims in
advertising be truthful, and evidence based.
F. Target Audience: a group of people who advertisers think
will buy or use the product. Advertisers create ads to persuade the target
audience to do, buy or think something. They also put their ads on the medium
where their target audience is likely to see it.
G. Advertising Techniques:
1. Endorsement:
Featuring someone like a celebrity saying how the product worked for them.
Example - When a start talks about his or her favorite product
2. Association:
Using images like a cartoon character or the American flag in the hope you will
transfer your good feelings about the image to the product. Example-a make-up
ad uses a beautiful model
3. Sense Appeal:
Using images and sounds to appeal to your senses – sight, touch, taste, etc…
Example – a fast food ad shows a close up of a burger
4. Call to action:
Tells you what to do. “Buy today” or “Call now”. Example – an ad asks you to
call or go online to find out more
5. Hype: Using
words like amazing and incredible make products seem really exciting. Example -
An ad for an exercise product promises “amazing results”
6. Repetition:
Repeating a message or idea so you remember it. Example – An announcer repeats
a product slogan
7. Claim:
Informing you about how the product works or helps you.
8. Humor: Using
ads that make you laugh can get your attention and be memorable.
9. Fear: Using a
product to solve something you worry about like body odor.
10. Sales &
Price: Showing or announcing a discounted price can make a product more
appealing.
11. Special
ingredients: Promoting a special ingredient in a product may persuade you
to think the product works better than the rest.
12. Games & Activities:
Making a commercial that is like a game will get you to spend more time getting
to know the product and influencing you to buy it.
13. Must-have:
Suggest you must have the product to be happy, popular or satisfied.
14. Prizes,
sweepstakes, and gifts: Using a chance to win a prize to attract attention
to a product. H.
Questions you should
ask yourself when watching an ad:
a. Who is responsible for the ad? b. What is the ad actually
saying?
c. What does the ad want me to do?
d. How much do I know about the product?
e. What do others who use the product think of it? O
f. Does the product fit into my budget?
g. Where else can I find information about the product?
OTHER TERMS TO KNOW:
VO: Signifies a voice over in a script
SOT: Signifies sound on tape in a script
VO/SOT: Usually used in News Production.
CG: Signifies title/graphics in a script
SUPER: Superimposition of title usually in lower
third of the screen.
SFX: Signifies special effects which could be
audio or video effects in a script.
ANNCR: Announcer
LS/WS: Long Shot or Wide Shot
CU: Close Up
XCU: Extreme
Close Up
MS: Medium Shot
OTS: Over the
Shoulder Shot
TRT: Total running time
WX: Stands for weather in a news script.
Soundbyte: The audio track portion of radio or TV
interview. These are usually no longer
than 15 seconds.
B-roll: Supplementary or alternative shots interwoven
in video editing with main shots.
Raw footage: Original unedited video footage captured
while shooting video.
We will also begin to work on Public Service Announcements this week.
Sunday, September 11, 2016
This week, students will wrap up writing, voicing, finding images and editing their videos documenting a copyright infringement case. The projects are due on Thursday 9/15.
We will take a test on Friday on the Advertising terms we learned about when working on our commercial projects. Students will receive the hand-out with all the terms, but if they lose it, they can always find it on my website.
Here is the link to the vocab for the test:
https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnxtcnN0aGVyaWF1bHRzdHZwcm9kdWN0aW9uY2xhc3N8Z3g6MzFhNjA2YTYxZDVjODUwMQ
Tuesday, September 6, 2016
Tuesday, August 30, 2016
Students will finish their commercial projects this week. We also will have a test on Thursday, September 1st, on the different kinds of camera shots, the rule of thirds and the 180 degree rule.
CAMERA SHOT
TYPES TERMS FOR TEST:
Six shots in Videographer’s Repertoire -
Long
shot, bust shot/head & shoulders shot, extreme close-up, medium shot,
close-up, over-the-shoulder
Long shot – Also known as an
establishing shot or wide shot it sets up the location of a video or film.
Bust shot/head & shoulder shot – Camera shot of an
actor/actress from waist up
Close up shot – The shot is tightly
framed on the subject so they dominate most of the frame and we can’t really
see what is going on in the background.
Extreme close up – Shows small details
of a subject that would not be noticed in a wider shot. It could be an extreme close up of an eye
crying or a wrinkled hand…
Medium shot – Shows most of the
subject’s body either from the waist up or the knees up.
Over-the-shoulder shot – Gives the
character’s point of view, but includes character’s shoulder or part of their
head. Commonly used when two characters
are having a discussion.
High Angle Shot - is a cinematic technique where the camera looks down on the
subject from a high angle and can
make the subject seem vulnerable or small or submissive when applied with the
correct mood, setting, and effects.
Low Angle
Shot - a shot from
a camera positioned low on the vertical
axis, anywhere below the eye line, looking up. Sometimes, the low-angle shot can make
the subject look strong and powerful.
Rule of
Thirds - The basic principle behind
the rule of thirds is to imagine breaking an image down into thirds (both
horizontally and vertically) so that you have 9 parts. As follows.
As you’re taking an image you would have done
this in your mind through your viewfinder or in the LCD display that you use to
frame your shot.
With this grid in mind the ‘rule of thirds’
now identifies four important parts of the image that you should consider
placing points of interest in as you frame your image.
Not only this – but it also gives you four
‘lines’ that are also useful positions for elements in your photo.
The theory is that if you place points of
interest in the intersections or along the lines that your photo becomes more
balanced and will enable a viewer of the image to interact with it more
naturally.
180 Degree Rule - is a cinematography guideline that
states that two characters in a scene should maintain the same left/right
relationship to one another . When the camera passes over the invisible axis
connecting the two subjects, it is called crossing the line and the shot
becomes what is called a reverse angle
Students will finish their commercial projects this week. We also will have a test on Thursday, September 1st, on the different kinds of camera shots, the rule of thirds and the 180 degree rule.
CAMERA SHOT
TYPES PROJECT:
You
and your partner(s) will check out a camera and shoot the 6 shots in the
videographer’s repertoire plus high angle and low angle shots for a total of 8
shots.
When
you are done shooting all 8 shots, you will upload the video clips to iMovie
and edit them.
Six shots in Videographer’s Repertoire -
Long
shot, bust shot/head & shoulders shot, extreme close-up, medium shot,
close-up, over-the-shoulder
Long shot – Also known as an
establishing shot or wide shot it sets up the location of a video or film.
Bust shot/head & shoulder shot – Camera shot of an
actor/actress from waist up
Close up shot – The shot is tightly
framed on the subject so they dominate most of the frame and we can’t really
see what is going on in the background.
Extreme close up – Shows small details
of a subject that would not be noticed in a wider shot. It could be an extreme close up of an eye
crying or a wrinkled hand…
Medium shot – Shows most of the
subject’s body either from the waist up or the knees up.
Over-the-shoulder shot – Gives the
character’s point of view, but includes character’s shoulder or part of their
head. Commonly used when two characters
are having a discussion.
High Angle Shot - is a cinematic technique where the camera looks down on the
subject from a high angle and can
make the subject seem vulnerable or small or submissive when applied with the
correct mood, setting, and effects.
Low Angle
Shot - a shot from
a camera positioned low on the vertical
axis, anywhere below the eye line, looking up. Sometimes, the low-angle shot can make
the subject look strong and powerful.
Rule of
Thirds - The basic principle behind
the rule of thirds is to imagine breaking an image down into thirds (both
horizontally and vertically) so that you have 9 parts. As follows.
As you’re taking an image you would have done
this in your mind through your viewfinder or in the LCD display that you use to
frame your shot.
With this grid in mind the ‘rule of thirds’
now identifies four important parts of the image that you should consider
placing points of interest in as you frame your image.
Not only this – but it also gives you four
‘lines’ that are also useful positions for elements in your photo.
The theory is that if you place points of
interest in the intersections or along the lines that your photo becomes more
balanced and will enable a viewer of the image to interact with it more
naturally.
180 Degree Rule - is a cinematography guideline that
states that two characters in a scene should maintain the same left/right
relationship to one another . When the camera passes over the invisible axis
connecting the two subjects, it is called crossing the line and the shot
becomes what is called a reverse angle
Sunday, August 21, 2016
Sunday, August 14, 2016
August 15-19th

8/15: We are going to review the 6 shots in the videographer’s
repertoire, the rule of thirds, and the 180
Degree Rule by watching video examples.
We will discuss Sound – microphones and techniques and Lens – focal length & depth of field
8/16: We will talk about white balance, exposure, auto focus
8/17-8/18: Lab days – shoot your original Vine video
showing the magic of creative shooting and editing. Incorporate 2-5 shots for the magic of
editing.
8/19: Watching
& critiquing projects
We will be having a test on 9/1 covering the items below:
Six shots in Videographer’s Repertoire -
Long
shot, bust shot/head & shoulders shot, extreme close-up, medium shot,
close-up, over-the-shoulder
Long shot – Also known as an
establishing shot or wide shot it sets up the location of a video or film.
Bust shot/head & shoulder shot – Camera shot of an
actor/actress from waist up
Close up shot – The shot is tightly
framed on the subject so they dominate most of the frame and we can’t really
see what is going on in the background.
Extreme close up – Shows small details
of a subject that would not be noticed in a wider shot. It could be an extreme close up of an eye
crying or a wrinkled hand…
Medium shot – Shows most of the
subject’s body either from the waist up or the knees up.
Over-the-shoulder shot – Gives the
character’s point of view, but includes character’s shoulder or part of their
head. Commonly used when two characters
are having a discussion.
High Angle Shot - is a cinematic technique where the camera looks down on the
subject from a high angle and can
make the subject seem vulnerable or small or submissive when applied with the
correct mood, setting, and effects.
Low Angle
Shot - a shot from
a camera positioned low on the vertical
axis, anywhere below the eye line, looking up. Sometimes, the low-angle shot can make
the subject look strong and powerful.
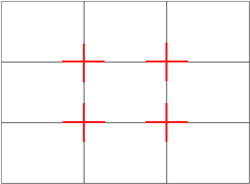
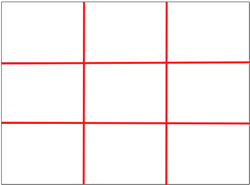
Rule of Thirds - The basic principle behind the rule of thirds is to imagine breaking an image down into thirds (both horizontally and vertically) so that you have 9 parts. As follows.

As you’re taking an image you would have done this in your mind through your viewfinder or in the LCD display that you use to frame your shot.
With this grid in mind the ‘rule of thirds’ now identifies four important parts of the image that you should consider placing points of interest in as you frame your image.
Not only this – but it also gives you four ‘lines’ that are also useful positions for elements in your photo.

The theory is that if you place points of interest in the intersections or along the lines that your photo becomes more balanced and will enable a viewer of the image to interact with it more naturally.
180 Degree Rule - is a cinematography guideline that states that two characters in a scene should maintain the same left/right relationship to one another . When the camera passes over the invisible axis connecting the two subjects, it is called crossing the line and the shot becomes what is called a reverse angle

Sunday, August 7, 2016
August 7-12
This week, we are going to go over some basic editing tips and will also get to shoot some video for the first time. We will also be tested on our classroom equipment safety procedures on Friday, August 12th. Below is a list of safety procedures / test study guide.
This week, we are going to go over some basic editing tips and will also get to shoot some video for the first time. We will also be tested on our classroom equipment safety procedures on Friday, August 12th. Below is a list of safety procedures / test study guide.
VIDEO PRODUCTION CLASSROOM SAFETY & PROCEDURES: (TEST AUGUST 12TH)
- Food and drink are not allowed near the computers or camera equipment.
- Classroom computers can only be used for educational purposes not for video games, or your internet searching pleasure.
- You must be extremely careful when using camera equipment and computers, it is fragile and breakable. The Video Production Classroom is a no nonsense zone!
- If you check-out gear and find something wrong, you must report it right away to the teacher.
- The teacher may be more lenient on a group that was honest about experiencing an accident while using the equipment than a group that tries to cover up a problem.
- The record button on the cameras also pauses what you’re recording.
- All camera equipment must be checked out before using it. You must fill out equipment check-out sheet and list the names of all in the group.
- After working with the camera equipment and uploading your videos to the computer, you must delete all videos before checking it back in and returning the equipment.
- Do not change camera settings without checking with the teacher first.
- While recording inside the classroom or in the hallway, you must not be too loud and disruptive to the other classes nearby.
- Everyone in the group must be working at all times.
- You should not run while using a camera or video equipment.
This week's project:
CAMERA SHOT TYPES:
Six shots in
Videographer’s Repertoire - Long shot, bust shot/head &
shoulders shot, extreme close-up, medium shot, close-up,
over-the-shoulder
Long shot – Also
known as an establishing shot or wide shot it sets up the location of a video
or film.
Bust shot/head &
shoulder shot – Camera shot of an actor/actress from waist up
Close up shot – The shot
is tightly framed on the subject so they dominate most of the frame and we
can’t really see what is going on in the background.
Extreme close up – Shows
small details of a subject that would not be noticed in a wider shot. It could be an extreme close up of an eye
crying or a wrinkled hand…
Medium shot – Shows
most of the subject’s body either from the waist up or the knees up.
Over-the-shoulder shot – Gives
the character’s point of view, but includes character’s shoulder or part of
their head. Commonly used when two
characters are having a discussion.
High Angle Shot - is a cinematic technique where the camera looks down on the
subject from a high angle and can
make the subject seem vulnerable or small or submissive when applied with the
correct mood, setting, and effects.
Low Angle
Shot - a shot from
a camera positioned low on the vertical
axis, anywhere below the eye line, looking up. Sometimes, the low-angle shot can make
the subject look strong and powerful.
You and your partner(s) will check out a camera and shoot the 6 shots in
the videographer’s repertoire.
When you are done shooting all six, you will upload the video clips to
iMovie and edit them.
Monday, August 1, 2016
It was great meeting my new students on the first day of school! Can't wait to see what videos they are going to be creating this year!
Please click on the online form to fill out the information form for students:
http://tinyurl.com/h8b93el
To get to know our level of proficiency, we are going to be taking a Kahoot survey:
https://play.kahoot.it/#/k/06eaeac9-290b-42be-8578-20d1541b3552
If you have any questions throughout the school year, feel free to email me at Vivian.Theriault@cobbk12.org
Please click on the online form to fill out the information form for students:
http://tinyurl.com/h8b93el
To get to know our level of proficiency, we are going to be taking a Kahoot survey:
https://play.kahoot.it/#/k/06eaeac9-290b-42be-8578-20d1541b3552
If you have any questions throughout the school year, feel free to email me at Vivian.Theriault@cobbk12.org
Wednesday, July 27, 2016
I am looking forward to meeting my new students at Pebblebrook High School. I have taught video production in Florida for the past 7 years. Before that, I worked for more than 10 years in television newsrooms across the country as a news anchor, reporter, producer, videographer and editor. I look forward to sharing my passion for digital story telling with my students.
Sign up for class related text notifications through remind.com. Go to: https://www.remind.com/join/mrsvthe
Sign up for class related text notifications through remind.com. Go to: https://www.remind.com/join/mrsvthe
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)